Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and robotics to create efficient, adaptive production environments central to Industry 4.0. They improve productivity, reduce costs, enhance product quality, enable mass customization, and promote sustainability.
Tan Thuan Export Processing Zone (“Tan Thuan EPZ”) in Ho Chi Minh City, established in 1991, spans 300 hectares and hosts over 254 companies from 22 countries. With state-of-the-art infrastructure and a focus on attracting high-tech and support high-tech manufacturing, Tan Thuan EPZ attracts leading companies in electronics, software development, and precision engineering. The zone also benefits from a rich talent pool for the high-tech industry, thanks to its proximity to numerous universities and technical schools. Leveraging the benefits of Tan Thuan EPZ's infrastructure and talented labor nearby, businesses can achieve significant growth and success in the high-tech industry by setting up a smart factory at here.
What is a Smart Factory?
Definition and key characteristics

What is smart factory
A smart factory is a highly digitized and connected production facility that relies on smart manufacturing technologies to enhance its processes. Unlike traditional factories, which often operate in silos, smart factories integrate various technologies and systems to create a seamless, automated, and intelligent production environment. Key characteristics of a smart factory include:
- Interconnectivity: Machines, devices, sensors, and people communicate and collaborate through the Internet of Things (IoT).
Automation: Automated systems and robotics perform repetitive, dangerous, or precision tasks, reducing the need for manual labor.
- Real-time data: Continuous data collection and analysis allow for immediate feedback and decision-making.
- Flexibility: The ability to quickly adapt to changes in production requirements or product designs.
- Optimization: Enhanced efficiency and resource management through predictive maintenance and data-driven insights.
Technologies involved
Smart factory leverages several advanced technologies to achieve their goals:
- Internet of things (IoT): Connects machinery, equipment, and systems to collect and share data, improving visibility and control over the production process.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Powers data analytics, machine learning, and decision-making processes, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing operations.
- Robotics: Automated robots perform complex tasks with high precision and speed, reducing human error and enhancing productivity.
- Automation: Systems that automatically control processes, machinery, and workflows, minimizing human intervention and increasing consistency.
- Big data analytics: Processes vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict trends, and make informed decisions.
- Cloud computing: Provides scalable and flexible IT resources, enabling real-time data access and collaboration.
Benefits of smart factory
The implementation of smart factory offers numerous benefits:

Smart factory at Tan Thuan EPZ
- Efficiency: Automation and real-time data analytics streamline operations, reducing production times and increasing throughput. This leads to faster time-to-market for products.
- Cost reduction: Predictive maintenance minimizes downtime and repair costs, while optimized resource usage reduces waste and energy consumption. These efficiencies lower overall operational costs.
- Quality improvement: Continuous monitoring and data analysis help maintain high product quality by identifying and correcting issues promptly. Automated systems ensure consistent production standards.
- Flexibility and customization: Smart factories can quickly adapt to changing market demands and customize products without significant downtime or retooling, meeting consumer preferences more effectively.
- Enhanced safety: Automation of hazardous tasks reduces the risk of accidents, creating a safer working environment for employees.
- Sustainability: Improved resource management and reduced waste contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices, aligning with environmental goals.
In summary, smart factory is transforming the manufacturing landscape by integrating advanced technologies to create efficient, flexible, and high-quality production environments. These innovations not only improve operational performance but also provide significant competitive advantages in the global market. Furthermore, the development of smart factories is a crucial aspect of attracting foreign direct investment in Vietnam, as they demonstrate the country's commitment to modernizing its industrial sector and enhancing its competitiveness on a global scale.
The Role of Universities and Vocational Schools in Developing Talent
Importance of education and training in the high-tech industry
The high-tech industry is constantly evolving, driven by rapid advancements in technology. To keep pace with these changes, a well-educated and highly skilled workforce is essential. Education and training programs play a crucial role in preparing individuals for careers in the high-tech sector by equipping them with the necessary knowledge and skills. Universities and vocational schools are at the forefront of this effort, offering specialized programs in engineering, computer science, robotics, and other relevant fields. By fostering a strong foundation in these areas, educational institutions ensure that graduates are ready to meet the demands of modern manufacturing and other high-tech industries.
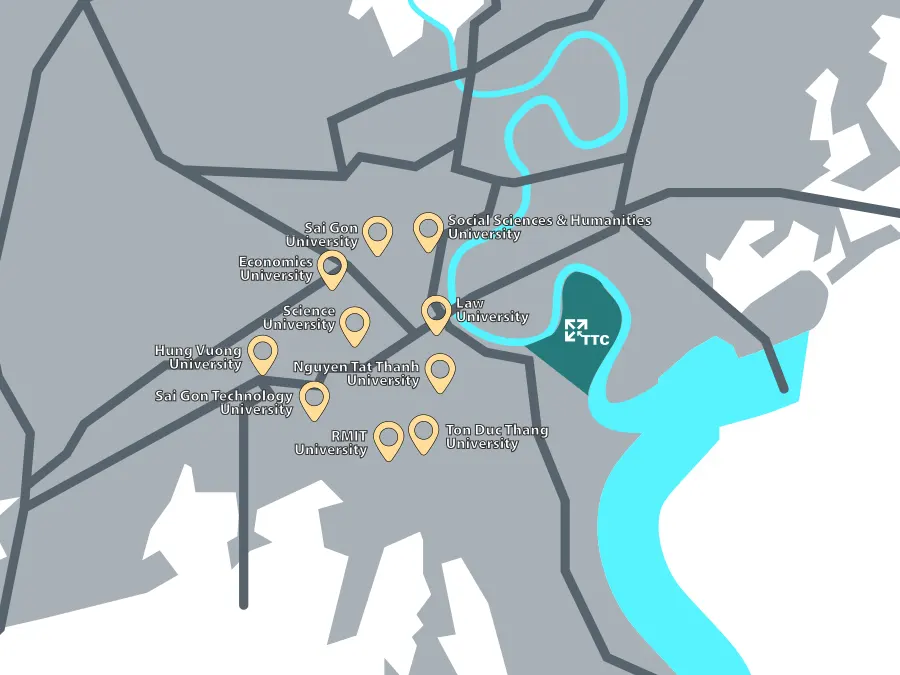
Tan Thuan EPZ near to universities in Ho Chi Minh city
Collaboration between industry and educational institutions
Collaboration between industry and educational institutions is vital for developing talent that meets the specific needs of the high-tech sector, including the growing field of smart factories. These partnerships provide several key benefits:
- Curriculum development: Industry input helps shape academic curricula to include the latest technological advancements and industry practices, ensuring that students are learning relevant and up-to-date skills. This is particularly important for the rapidly evolving smart factory landscape.
- Hands-on experience: Internship and apprenticeship programs offer students practical experience, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings. This hands-on training is invaluable for understanding the complexities of modern manufacturing environments, including those in smart factories.
- Research and innovation: Collaborative research projects between universities and companies drive innovation, with students and faculty working on cutting-edge technologies and solutions that can be implemented in the industry, such as those found in smart factories.
- Talent pipeline: These partnerships create a direct pipeline for recruiting new talent. Companies can identify and hire top-performing students, while graduates benefit from increased job opportunities and smoother transitions into the workforce, particularly in the smart factory sector.
Examples of successful partnerships
Numerous successful partnerships between educational institutions and industries highlight the benefits of such collaborations:
- MIT and Boeing: The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Boeing have a long-standing partnership focused on aerospace innovation. Through joint research initiatives, internships, and collaborative projects, students gain exposure to advanced aerospace technologies and industry practices, while Boeing benefits from cutting-edge research and a steady stream of skilled graduates.
- Siemens and Technical University of Munich: Siemens collaborates with the Technical University of Munich (TUM) on various projects related to digitalization and automation. This partnership includes joint research labs, student internships, and funding for academic programs. As a result, TUM students gain valuable insights into industrial applications of their studies, and Siemens accesses a pool of talented engineers and researchers.
- General Electric and Local Community Colleges: General Electric (GE) has partnered with several community colleges across the United States to develop specialized training programs in advanced manufacturing. These programs include coursework in robotics, automation, and data analytics, along with hands-on training at GE facilities. This collaboration helps bridge the skills gap in the manufacturing sector and provides students with direct pathways to employment at GE.
- Intel and Arizona State University: Intel and Arizona State University (ASU) have established a partnership to advance semiconductor research and education. Intel supports ASU with funding for research projects, internships, and scholarships. In turn, ASU provides Intel with access to cutting-edge research and a talent pool of students trained in semiconductor technologies.
- FPT Software and Vietnamese Universities: FPT Software, a leading technology company in Vietnam, collaborates with several Vietnamese universities to develop IT and software engineering programs. These partnerships include curriculum development, internship opportunities, and joint research projects. FPT Software benefits from a steady supply of well-trained graduates, while students gain practical experience and job opportunities in the high-tech industry.
In summary, universities and vocational schools play a pivotal role in developing the talent needed for the high-tech industry, including the smart factory sector. Through collaborations with industry, these institutions ensure that their programs are aligned with the latest technological advancements and industry needs, providing students with the education and experience necessary to succeed in their careers. These partnerships not only benefit students and educational institutions but also help companies stay competitive by securing a skilled workforce and driving innovation in smart factory technologies.
Additionally, these collaborations are instrumental in attracting foreign direct investment in Vietnam, showcasing the country's commitment to advancing its industrial sector and supporting high-tech manufacturing.
Tan Thuan Export Processing Zone: A Hub for Innovation
History and development of the Tan Thuan Export Processing Zone
Established in 1991, Tan Thuan EPZ was the first export processing zone in Vietnam. It has grown into a premier industrial hub, covering 300 hectares and including an Export Processing Zone, Industrial park, Commercial Area, and E-Office Park.
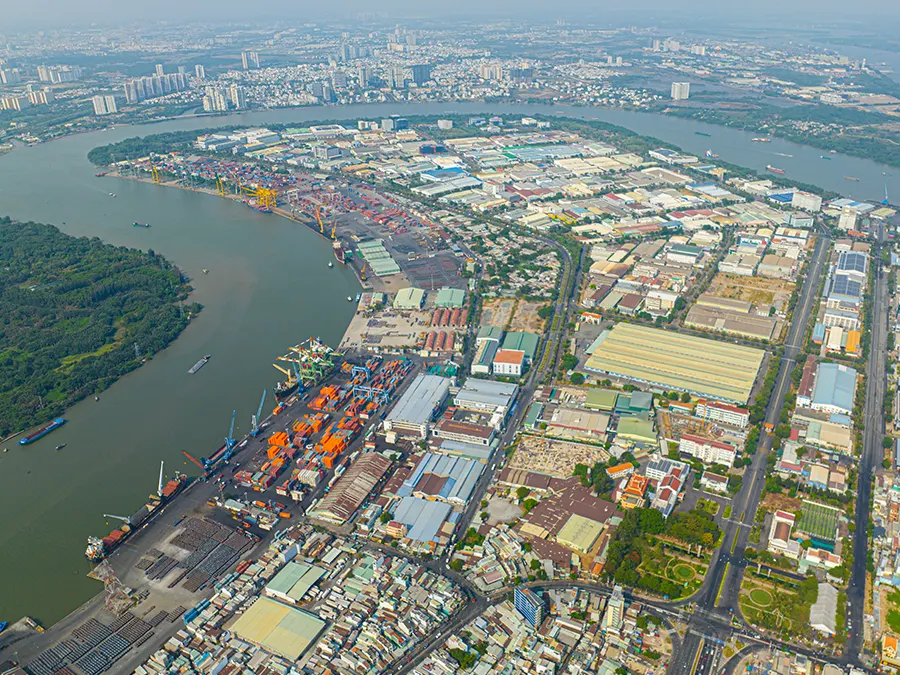

Tan Thuan Export Processing Zone
Advantages of setting up operations in Tan Thuan
- Location: Strategic proximity to the city center and major transportation networks, including Tan Son Nhat International Airport and key seaports: Cat Lai International Port and VICT international Airport.
- Infrastructure: State-of-the-art facilities and reliable utilities.
- Incentives: Attractive investment incentives and comprehensive support services.
Trends and predictions for the next decade
- Increased automation: Greater reliance on robotics and AI for manufacturing processes.
- Advanced analytics: Enhanced use of big data and predictive analytics to optimize operations.
- Sustainability: Continued focus on environmentally friendly practices and resource efficiency.
Potential impact on the local and national economy
Smart Factories that are set up in Tan Thuan will drive economic growth by attracting high-tech investments, creating high-skilled jobs, and increasing export revenues. This will contribute to Vietnam’s position as a global manufacturing hub.
Government policies and incentives will be crucial in supporting the development of smart factories. This includes:
- Investment in Education: Enhancing STEM education and vocational training.
- Regulatory Support: Creating a favorable regulatory environment for high-tech industries.
- Financial Incentives: Providing tax breaks and subsidies to encourage investment in smart manufacturing technologies.
Learn more: Standard Factories F.G.H
In conclusion, Tan Thuan EPZ is a prime investment destination for businesses looking to set up Smart Factories. Located in the city center and in close proximity to leading universities that produce top talent in modern technology, Tan Thuan EPZ offers not only comprehensive infrastructure but also an excellent working environment for employees in the 4.0 industry. This combination will significantly enhance the growth and competitiveness of Tan Thuan Export Processing Zone and Vietnam’s high-tech industry.